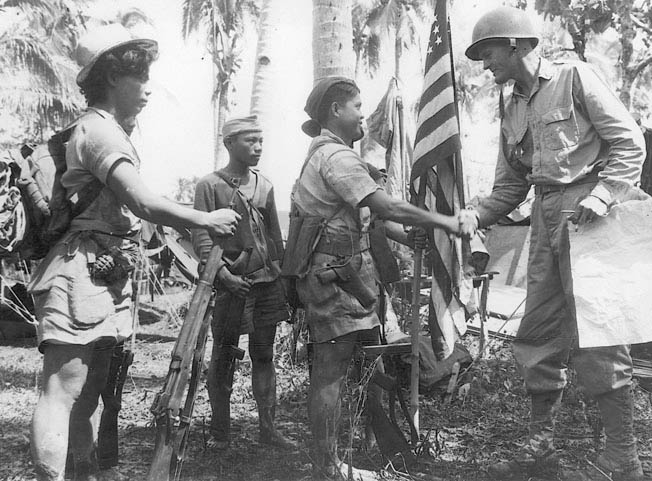
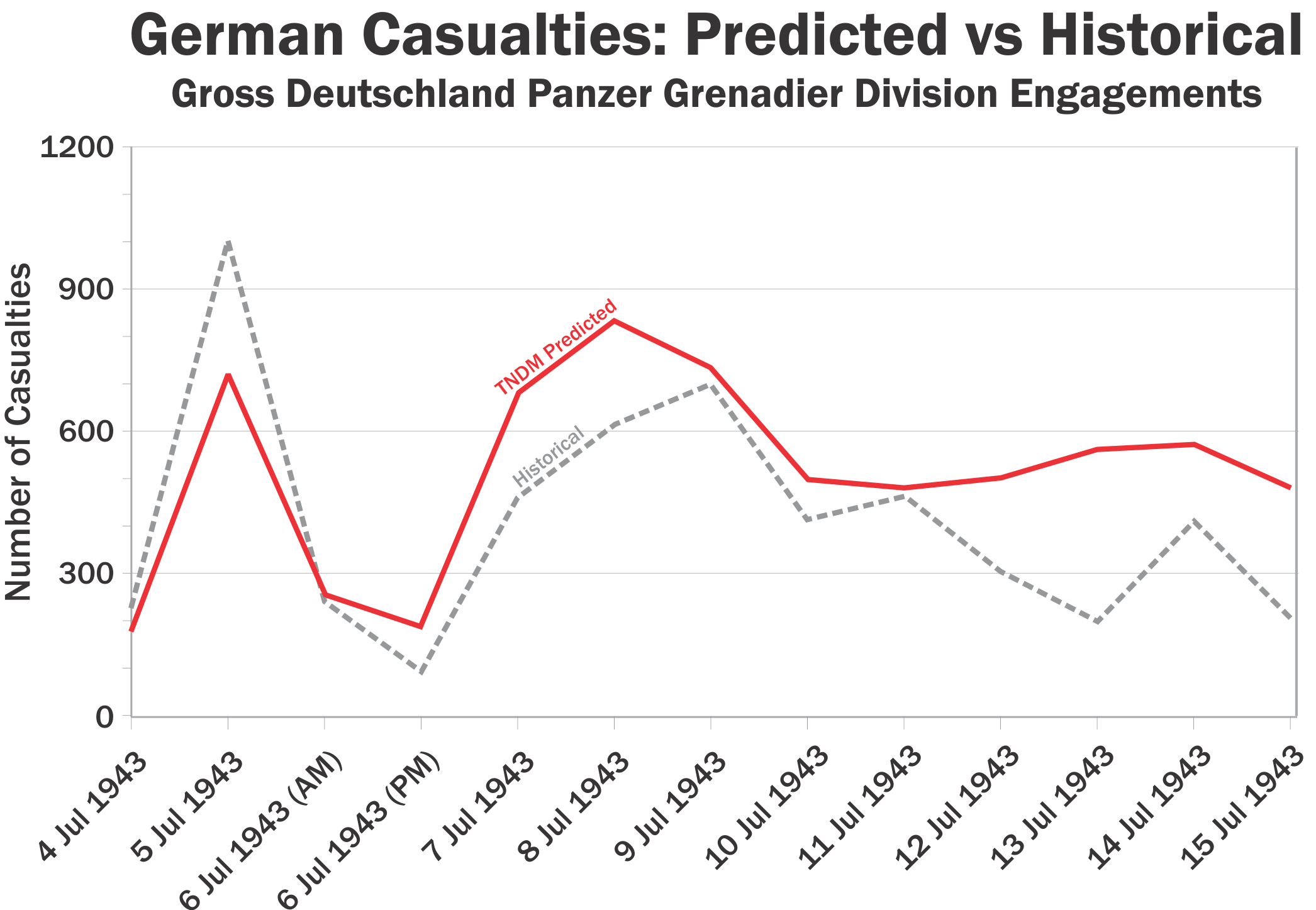
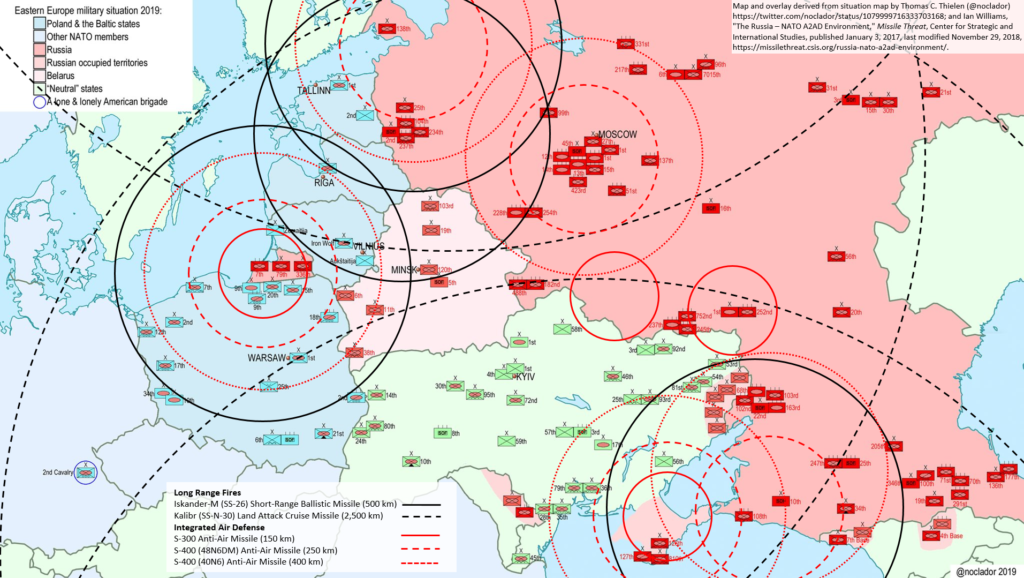
U.S. Army Major Amos Fox has recently published the first two of a set of three articles examining nature of proxy warfare in the early 21st century and suggests some ideas for how the U.S. might better conduct it.
In “In Pursuit of a General Theory of Proxy Warfare,” published in February 2019 by the The Institute of Land Warfare at the Association of the U.S. Army, and “Time, Power, and Principal-Agent Problems: Why the U.S. Army is Ill-Suited for Proxy Warfare Hotspots,” published in the March-April 2019 edition of Military Review, Fox argues,
Proxy environments dominate modern war… It is not just a Russian, Iranian or American approach to war, but one in which many nations and polities engage. However, the U.S. Army lacks a paradigm for proxy warfare, which disrupts its ability to understand the environment or develop useful tactics, operations and strategies for those environments.
His examination of the basic elements of proxy warfare leads him to conclude that “it is dominated by a principal actor dynamic, power relationships and the tyranny of time.” From this premise, Fox outlines two basic models of proxy warfare: exploitative and transactional.
The exploitative model…is characterized by a proxy force being completely dependent on its principal for survival… [It] is usually the result of a stronger actor looking for a tool—a proxy force—to pursue an objective. As a result, the proxy is only as useful to the principal as its ability to make progress toward the principal’s ends. Once the principal’s ends have been achieved or the proxy is unable to maintain momentum toward the principal’s ends, then the principal discontinues the relationship or distances itself from the proxy.
The transactional model is…more often like a business deal. An exchange of services and goods that benefits all parties—defeat of a mutual threat, training of the agent’s force, foreign military sales and finance—is at the heart of the transactional model. However, this model is a paradox because the proxy is the powerbroker in the relationship. In many cases, the proxy government is independent but looking for assistance in defeating an adversary; it is not interested in political or military subjugation by the principal. Moreover, the proxy possesses the power in the relationship because its association with the principal is wholly transactional…the clock starts ticking on the duration of the bond as soon as the first combined shot is fired. As a result, as the common goal is gradually achieved, the agent’s interest in the principal recedes at a comparable rate.
With this concept in hand, Fox makes that case that
[T]he U.S. Army is ill-suited for warfare in the proxy environment because it mismanages the fixed time and the finite power it possesses over a proxy force in pursuit of waning mutual interests. Fundamentally, the salient features of proxy environments—available time, power over a proxy force, and mutual interests—are fleeting due to the fact that proxy relationships are transactional in nature; they are marriages of convenience in which a given force works through another in pursuit of provisionally aligned political or military ends… In order to better position itself to succeed in the proxy environment, the U.S. Army must clearly understand the background and components of proxy warfare.
These two articles provide an excellent basis for a wider discussion for thinking about and shaping not just a more coherent U.S. Army doctrine, but a common policy/strategic/operational framework for understanding and successfully operating in the proxy warfare environments that will only loom larger in 21st century international affairs. It will be interesting to see how Fox’s third article rounds out his discussion.

 The December 2018 issue of
The December 2018 issue of 

 While perusing Charles Shrader’s fascinating
While perusing Charles Shrader’s fascinating