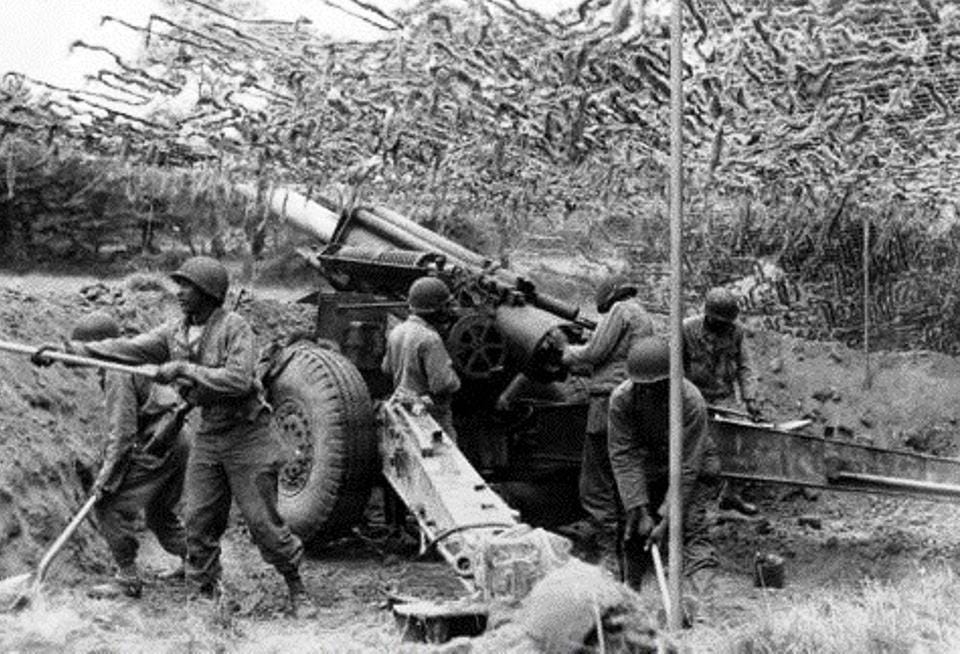
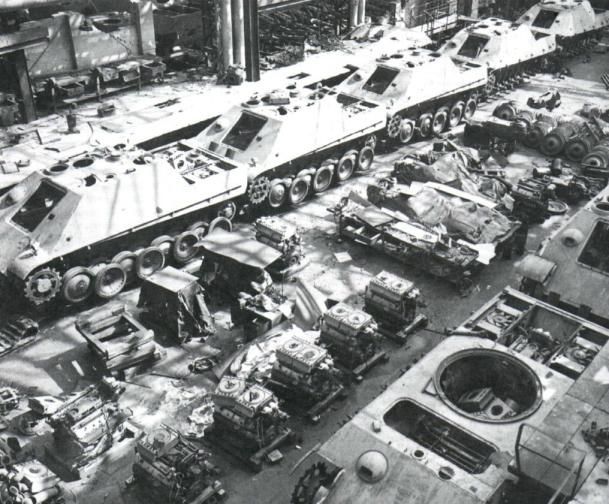
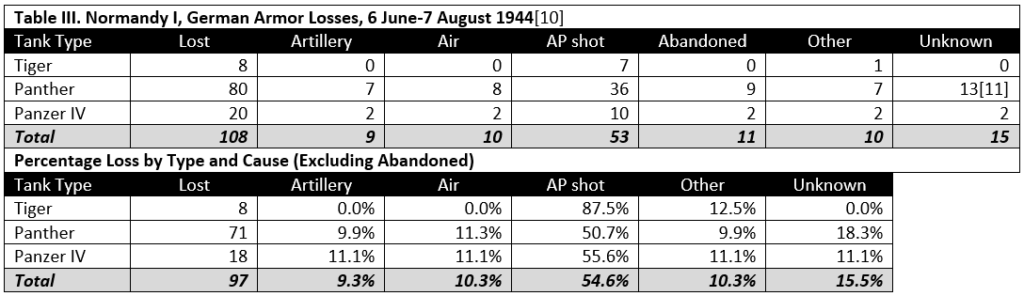
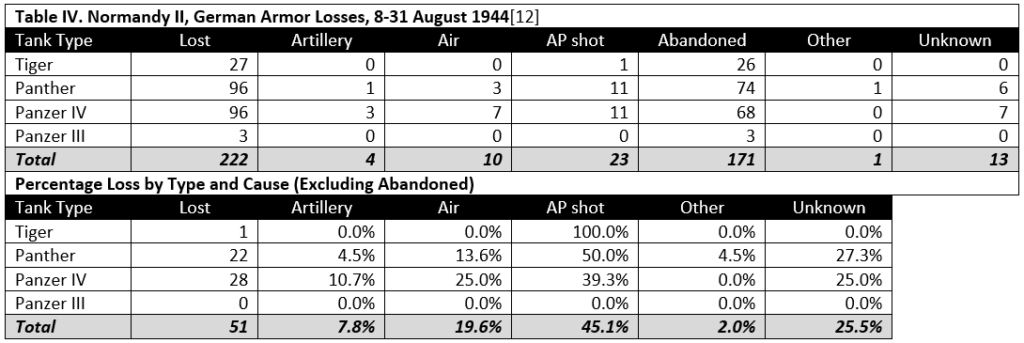
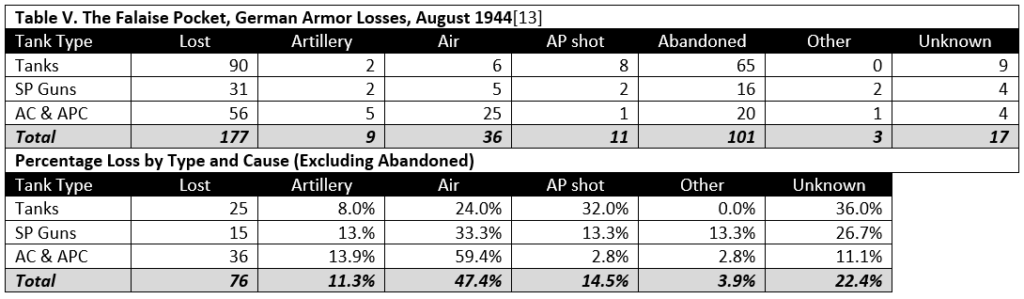
The 654th Jagdpanther battalion fought in Normandy, on the eastern part of the front. Unlike most German battalion level records, the war diary plus annexes has survived for this unit. At battalion level, the fate of many tanks can often be tracked and this unit is no exception. Included in the annexes is a list of the Jagpanthers lost by the battalion, by chassis number or turret number and which includes date (and often time as well), location, cause, list of items recovered, etc. All information is taken from the war diary and its annexes.
When it started marching from Rocquigny near the Belgian border towards Normandy, it had 25 Jagdpanthers, On 27th July, three command Panthers and one Jagdpanther arrived at the battalion. They first had to be checked by the workshops and on July 29 they were ready for action.
Marching to Normandy took its toll of the battalion. There were several air attacks, which caused losses in the battalion, but none of the Jagdpanthers were destroyed. However, many Jagdpanthers suffered mechanical breakdowns. During the march (approx. 300 km) the following cases of damage was recorded: 18 final drives (a well-known problem), two engines, 2 oil coolers, 3 cooling fans, 1 torsion bar, 4 road wheels, 1 drive shaft, 4 drive sprockets, 2 idler wheels and 109 track links.
The result was that on July 17, the battalion had 8 operational Jagdpanther, 16 in short repair and 1 in long repair. Efforts by the repair and recovery services raised the operational readiness to 23 Jagdpanther on 30 July, 2 in long repair and 1 long repair. This includes one additional Jagdpanther that arrived on this day. Until July 26, the following damage had been caused by enemy action: 1 gear box, 4 radiators, 1 oil cooler, 4 cooling fans, 6 drive sprockets, 2 final drives, 16 road wheels.
It is unclear how many vehicles that were damaged up to this point, as single vehicles could have suffered more than one kind of damage. For example, a hit on a tank could cause damage to more than one road wheel. Before July 31, no Jagdpanther was completely lost.
The 2nd Coy arrived ahead of the rest of the battalion at the front in Normandy and it reported 6 operational Jagdpanther on July 7, when attached to the Panzer-Lehr division. It was however attached to 276th ID when Pz-Lehr left its sector. When moving on July 8, four Jagdpanthers broke down. Two more broke down on July 9, but four were also repaired. On July 11, one Jagpanther was penetrated in the left side armour and three crew members were wounded, but no other damage was recorded. Also, another Jagpanther was penetrated (does not say from which direction). The loader was killed and the commander, driver and gunner were wounded. The crew still managed to drive the tank into safety.
At least one Jagpanther was repaired by the company between 12 and 17 July.
Given the increase in operational Jagpanthers from July 17 and 29 at least 14 must have been repaired. At least five were repaired by 2nd Coy before July 17. So far we have indications of 19 repairs. However, there were further Jagdpanthers damaged between July 18 and 29. On July 20, two were damaged by enemy artillery fire and classified as short repair. Two days later, a periscope on one Jagdpanther was destroyed by enemy artillery fire. On July 26 one Jagdpanther caught fire in the engine room, not by enemy action. Vehicle classified as short repair. Four days later, one Jagdpanther was damaged by artillery fire and classified as short repair.
There were at least five vehicles damaged in this period when the operational readiness rose due to the efforts of the mechanics. We can conclude that at least 24 had been repaired before July 31. But this cannot possibly account for all vehicles damaged Also, it is clear that the kind of damage sustained thus far was of a kind that ought to be repaired and it can safely be assumed that more than 100 % of its Jagdpanthers had been in repair and not a single one had been lost.
P.S. The picture was drawn from this article: http://www.tanks-encyclopedia.com/ww2/nazi_germany/Jagdpanther.php