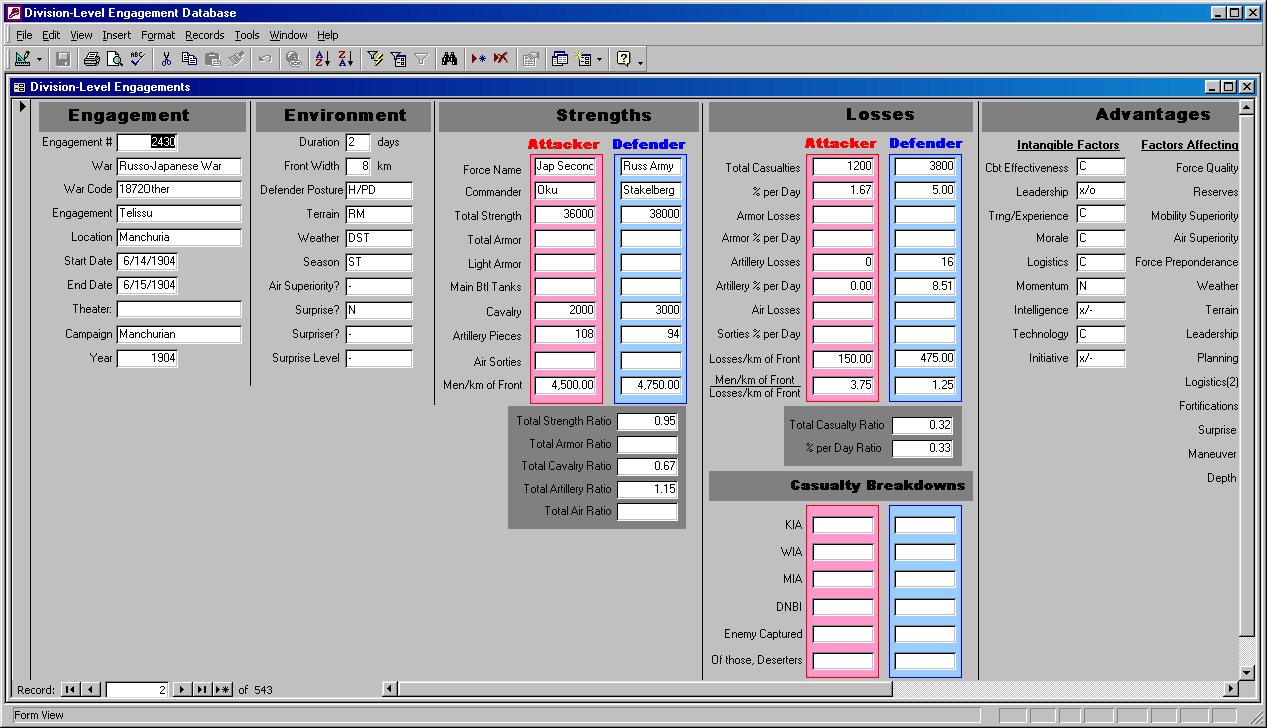
As I result of a discussion I am having about Kursk with Niklas Zetterling, I have decided to compare the actual repair and replacement efforts of the Soviet II Guards Tank Corps to the German Totenkopf (Death’s Head) SS Panzer Grenadier Division. The II Guard Tank Corps was selected as it has some of the more complete records and it maintained its position in the “Donets triangle” from the beginning of the battle on 5 July 1943 until the 15th of July 1943. Its headquarters at Kosukhin on 4 July (can’t locate), it was at Kalinin on 6 July (305455?), and it was at Sazhnoye (3734) by 0700 7 July, moved to Kleimenovo (4037) by 0700 10 July, moved to Plota (4345) by 0700 11 July, moved to Zhilomostnoye (4048) by 0700 12 July, and moved to Bereznik (490555), 3 km east of Krasnoye by 0700 15 July. The unit was never overrun or forced back by an attack, so it was in a decent position to repair and replace tanks.
As I result of a discussion I am having about Kursk with Niklas Zetterling, I have decided to compare the actual repair and replacement efforts of the Soviet II Guards Tank Corps to the German Totenkopf (Death’s Head) SS Panzer Grenadier Division. The II Guard Tank Corps was selected as it has some of the more complete records and it maintained its position in the “Donets triangle” from the beginning of the battle on 5 July 1943 until the 15th of July 1943. Its headquarters at Kosukhin on 4 July (can’t locate), it was at Kalinin on 6 July (305455?), and it was at Sazhnoye (3734) by 0700 7 July, moved to Kleimenovo (4037) by 0700 10 July, moved to Plota (4345) by 0700 11 July, moved to Zhilomostnoye (4048) by 0700 12 July, and moved to Bereznik (490555), 3 km east of Krasnoye by 0700 15 July. The unit was never overrun or forced back by an attack, so it was in a decent position to repair and replace tanks.
The Totenkopf was selected as it was the German armor unit nearest to it and engaged with it. The Totenkopf SS Division ended up holding down the SS Panzer Corps right flank until the 9th, when it then moved up to cross the Psel River and try to take Prokhorovka from the north-northwest.
So lets look at Totenkopf for a moment (this is data from the Kursk Data Base):
Date Tank Strength* Destroyed Damaged In Repair Returned to Duty
7/04 165 0 0 11
7/05 150 1 14
7/06 139 3 8
7/07 133 1 7 2
7/08 122 2 9 0
7/09 105 4 15 2
7/10 116 0 0 11
7/11 134 0 3 21
7/12 106 3 25 0
7/13 77 2 27 0
7/14 76 2 6 7
7/15 80 0 1 5
7/16 97 0 0 17
7/17 98 0 2 3
7/18 96 0 2 0
Total 18 119 68
* On 4 July this tank strength consisted of 59 Pz III long, 8 Pz III Command, 7 Pz IV short, 40 Pz IV long, 11 Pz VI, 1 Pz VI Command, 28 SuG III and 11 Marder IIs. AFVs not included in this count are 5 Pz III Observation, 5 Hummel, 12 Wespe, 36 armored cars, 56 light halftracks (including 3 250/10 with 37mm AT) and 69 medium halftracks (including 2 251/9 with 75mm lt IG and 7 251/10 with 37mm AT).
Strength figures are nominally as of 1800 on that day.
It appears that around 13% of the tanks destroyed/damaged/broken-down were written-off as destroyed. The Totenkopf SS Division appears to have repaired 57% of the damaged tanks during this time (and they may have repaired more later).
Now, let us look at the II Guards Tank Corps (also data from the Kursk Data Base)
Date Tank Strength Destroyed Damaged In repair Returned to Duty
7/04 187 * 0 0 30 ** 0
7/05 187 0 0 30 0
7/06 159 17 11 41 0
7/07 171 0 7 29 ** 19 T-34s **
7/08 155 6 10 39 0
7/09 133 7 23 54 5-8 Churchills ***
7/10 139 0 2 48 8
7/11 140 3 2 44 6 (4 Churchills)
7/12 82 24 35 78 0-1 Churchill
7/13 80 1 4 3
7/14 59 13 8 0
7/15 57 2 14 14 T-34s ****
7/16 63 0 0 6 ****
7/17 63 0 0 0
7/18 31 9 25 2
Total 82 141 63-67
Less tanks that were probably not repaired: – 19
Less the confusing Churchill reports: – 9 – 13
Total returned to duty (RTD) was probably around: 35
* On 4 July this tank strength consisted of 99 T-34s, 72 T-70s and 16 Churchills. The unit also had 28 BA-64 (armored cars) and 20 Bren Gun Carriers. Note that there is another report that records the corps on 4 July as having 121 T-34s, 75 T-70s, 21 Churchills (Fond: 2nds GTC, Opis: 1, Delo: 23, pages 4-9). We believe this is total tanks, not just tanks ready-for-action.
It appears that around 37% of the tanks destroyed/damaged/broken-down were written-off as destroyed. The II Guards Tank Corps appeared to repair 45% of the damaged tanks during this time (and they may have repaired more later), but as 28 of these repairs were probably not repaired tanks (see the ** and *** remarks below), then it appears that they repaired around 25% of the damaged tanks during this time.
So, compared to the Germans, the Soviet unit wrote off a higher percentage of tanks written off as destroyed (13% versus 37%) and a lower percentage of damaged tanks repaired (57% repaired versus 25% repaired). This is pretty typical for all the German panzer and panzer grenadier divisions compared to Soviet tank and mechanized corps at Kursk. Also, most of the Soviet repaired arrived on the 15th and 16th, after the battle was winding down.
——————————————————————————————————————–
P.S. The map is of the II Guards Tank Corps operation on 6 July 1943 from page 475 of my book. It is the II Guards Tank Corps map for 1800, 6 July 1943.
P.P.S.: The remaining notes are here:
** These tanks almost certainly are reserve T-34s, vice recently repaired ones. In operational report #181, dated 0700 8 July, they list a corps reserve of 20 T-34s and 10 T-70s. They state that “the 20 tanks in corps reserve are located in Bubnovo.” I have yet to locate Bubnovo on a map.The keeping of 20 or 30 spared tanks was a normal practice at Kursk at this time. The difference between the ready-for-action reports and other tank counts on 4 July do indicate that there was a spare 22 T-34s, 3 T-70s, and 5 Churchills with the unit (see the * remark). The 19 RTD tanks are certainly the 20 spare tanks activated. This is the only mention of the “corps reserve’ in the II Guards Tank Corps records we have.
*** These are all Churchills. From 7/09 through 7/12 we have 9-13 Churchills RTD. The actual report of Churchill strength and losses from 7/08 – 7/13 is confusing:
0700 7/08: 1. 5 Churchills at 2400 July 7
2. Combat ready tanks: 5 Churchills (from 2 reports)
0700 7/09: 1. 5 Churchills.
2. Losses on July 8: 2 Churchills burned, 3 Churchills knocked out.
0700 7/10: 1. “The regiment suffered losses, including 2 Churchills burned, out of 5 combat-ready.”
2. “47ths Gds Heavy Tank Rgt, with 3 Churchills is in the area of Khokhlovo….”
3. On July 9 the corps lost 1 Churchill burned and 1 Churchill knocked out.
4. Combat ready tanks: 3 Churchills (2 reports)
5. Corps lost 5 Mk-4s on 9 July (from a different report)
0700 7/11: Combat ready tanks: 3 Churchills (2 reports)
0700 7/12: 1. “47th Gds Heavy Tank Rgt, with 6 Churchills…”
2. At 2400 on July 11…..47th Gds Heavy tank Rgt, consisting of 2 Churchills, is in the corps commander reserve north of Leski.
3. Corps losses for July 11: 3 Churchills burned, 2 Churchills knocked out.
4. Combat Ready Tanks: 2 Churchills (2 reports)
0700 7/13: Report is missing
0700 7/14: Combat Ready Tanks: 2 Churchills
The unit, the 47th Guards Heavy Tank Regiment, was operating independent of the corps, having gotten separated on the 7th and moved over to face the III Panzer Corps. It appear unlikely over these three days that 16-19 Churchills were damaged or broken down, and that 13-16 of them were repaired, but this is the only way to get totals to work. It is either that assumption, or one has to dismiss some parts of the records as in error, and it is hard to know what to dismiss. This is most likely anomalous data in the II GTC records.
**** These 14 tanks we believe are repaired. they reported at 0700 15 July to have combat-ready 30 T-34s, 12 T-70s, and 2 Churchills, they report losses for 15 July of 6 T-34s knocked out, 1 T-34 burned, 2 T-70s knocked out, 1 burned (10 tanks total) and they reported on 0700 16 July combat-ready 45 T-34s, 18 T-70s. Another report for the 16th states that “following repairs, the corps had the following tanks in line: 38 T-34s and 15 T-70s.”
P.P.P.S. The Totenkopf SS Division lost around 57 tanks on 12th and 13th of July (and we don’t know how many were actually lost on what given day). Some authors, in their accounts of Prokhorovka seem to ignore its efforts and its losses, even though it was engaged with elements of Rotmistrov’s Fifth Guards Tank Army and its objective was Prokhorovka (which it did not achieve).

 As I result of a discussion I am having about Kursk with Niklas Zetterling, I have decided to compare the actual repair and replacement efforts of the Soviet II Guards Tank Corps to the German Totenkopf (Death’s Head) SS Panzer Grenadier Division. The II Guard Tank Corps was selected as it has some of the more complete records and it maintained its position in the “Donets triangle” from the beginning of the battle on 5 July 1943 until the 15th of July 1943. Its headquarters at Kosukhin on 4 July (can’t locate), it was at Kalinin on 6 July (305455?), and it was at Sazhnoye (3734) by 0700 7 July, moved to Kleimenovo (4037) by 0700 10 July, moved to Plota (4345) by 0700 11 July, moved to Zhilomostnoye (4048) by 0700 12 July, and moved to Bereznik (490555), 3 km east of Krasnoye by 0700 15 July. The unit was never overrun or forced back by an attack, so it was in a decent position to repair and replace tanks.
As I result of a discussion I am having about Kursk with Niklas Zetterling, I have decided to compare the actual repair and replacement efforts of the Soviet II Guards Tank Corps to the German Totenkopf (Death’s Head) SS Panzer Grenadier Division. The II Guard Tank Corps was selected as it has some of the more complete records and it maintained its position in the “Donets triangle” from the beginning of the battle on 5 July 1943 until the 15th of July 1943. Its headquarters at Kosukhin on 4 July (can’t locate), it was at Kalinin on 6 July (305455?), and it was at Sazhnoye (3734) by 0700 7 July, moved to Kleimenovo (4037) by 0700 10 July, moved to Plota (4345) by 0700 11 July, moved to Zhilomostnoye (4048) by 0700 12 July, and moved to Bereznik (490555), 3 km east of Krasnoye by 0700 15 July. The unit was never overrun or forced back by an attack, so it was in a decent position to repair and replace tanks.