Page 10 for War by Numbers includes the following table:
European Theater of Operations (ETO) Data, 1944
Force Ratio Result Percent Failure Number of cases
0.55 to 1.01-to-1.00 Attack Fails 100% 5
1.15 to 1.88-to-1.00 Attack usually succeeds 21% 48
1.95 to 2.56-to-1.00 Attack usually succeeds 10% 21
2.71-to-1.00 and higher Attacker Advances 0% 42
Many commercial wargames have something called a CRT or Combat Results Table. It is based upon force ratios. For example, this was one of the earliest CRTs used on Avalon Hill Games in the 1960s.
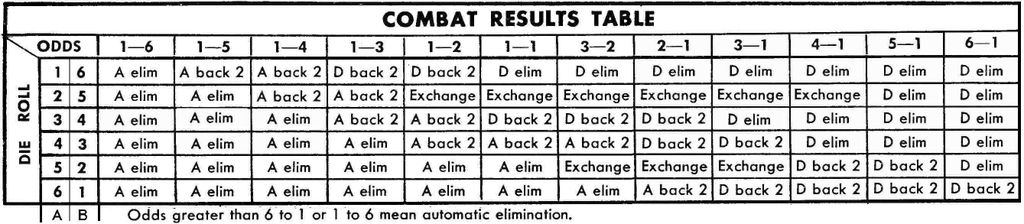
As can been seen from this Combat Results Table, at 1-to-1 the chances of an attack winning is one-in-three. At 2-to-1 odds the chances of the attacker winning is either the same as the defender winning or is a two-thirds chance of winning. At 3-to-1 odds, the attacker will always win.
Now the variable factor is the exchange result, which is defined that the defender removed everyone and the attacker removes as much as the defender. This usually results in an attacker win, if the attack has the right “spare change.” If the attacker was attacking with a single 7 strength unit against a 3 strength defender and they roll and exchange, then both units are eliminated.
Compare that to the table from my book based upon 116 division-level engagements from the European Theater of Operations (1944-145).
Needless to say, some elements of my book War by Numbers are of interest to the commercial wargaming community.

Chris, I hope that you have forwarded that message to the wargaming companies still in existence. (We’ll have to refight those battles for which your attacks defeated my defenses; of course, only for battles fought after you taught me to fight in battle lines rather than fight from strong points : – )
Chris,
I think this is a good point, but I have questions.
1. How do you define attack “usually”? If it usually succeeds, then the ratio of attack/defeat could be succeeds? Or is that why you say the attack fails a certain percentage?
2. A successful attack always advances because it seizes its objective. Does Attacker Advances mean he broke through or exploited?