
In my first post on Japan’s grand strategy, I examined its “free and open” Indo-Pacific policy and briefly reviewed its armed forces—nominally “self-defense forces (SDF)”—as well as the legal reasons for this euphemism, and the Japanese government’s plans to clarify this constitutional conundrum.
The next several posts in this series will focus on a general overview of the Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF), why this branch is considered primary (or dominant), some history in terms of how it came to be, the current missions, defense concepts, current capabilities and how they have been envisioned, how they are deployed, and a look ahead about options under consideration.
According to an excellent article in the Naval War College Review by Toshi Yoshihara, “the Japanese often describe their key national characteristic in nautical terms, with the familiar notion that ‘Japan is a small island nation lacking resource endowments and is thus highly dependent upon seaborne commerce for its well-being.’”
A few key facts, according to Jane’s Defense: Sea Module:
- Japan has the world’s seventh-largest Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Japan operates a large commercial fishing fleet of about 200,000 vessels.
- 90% of Japan’s oil is shipped from the Middle East.
- 60% of Japan’s food is imported by sea.
The JMSDF is therefore tasked with the fundamental naval missions of defending Japan from maritime invasion and securing the sea lines of communication (SLOC). A recent article in the Japan News, spelled out why SLOC protection is vital for Japan:
[T]he South China Sea is a key sea-lane for Japan. If it became necessary to take a detour around the South China Sea, the additional time and fuel costs are estimated to be 1½ days and $120,000 for travel via the Sunda Strait, and three days and $240,000 for travel via the Lombok Strait. Both of these straits can be perilous, with strong tidal currents, sunken ships and shoals. If either were to see a large increase in marine traffic, chaos is predicted to ensue.
We can see this concern clearly in the recent JMSDF exercise deployment through the South China Sea, the straits of Sunda and Malacca, and onwards to India.
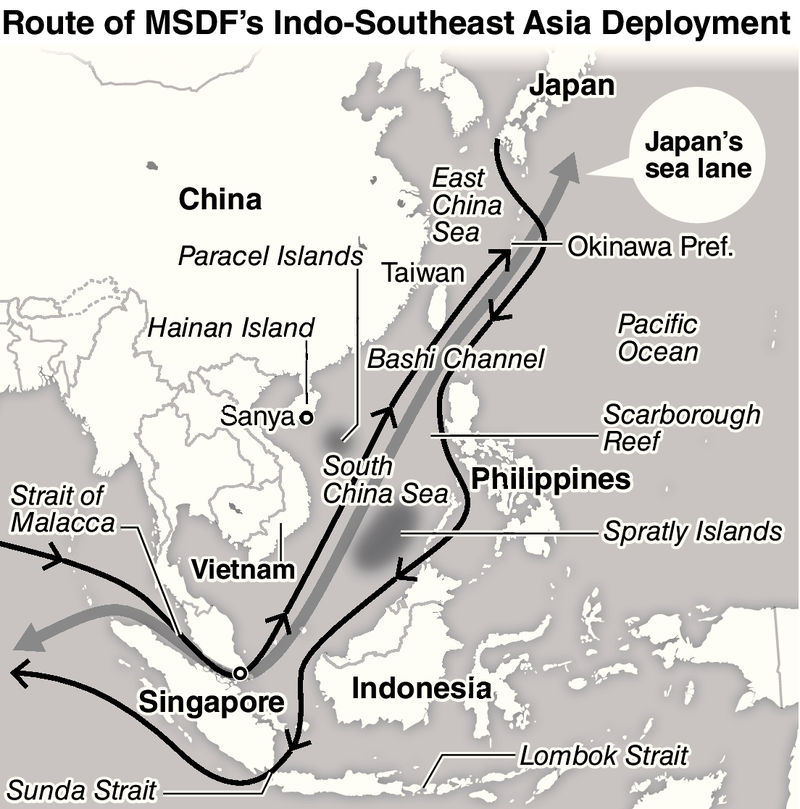
For Indo Southeast Asia Deployment 2018 (ISEAD18) from 26 August to 30 October 2018, JMSDF vessels JS Kaga (DDH 184), JS Inazuma (DD105), JS Suzutsuki (DD117), stopped at Subic Bay, Philippines; Jakarta, Indonesia; Colombo, Sri Lanka; Visakhapatnam, India; and Changi, Singapore. The exercise included naval various exercises with port call countries, as well as the British and U.S. navies. This activity yielded important agreements, such as the maritime surveillance pact between Japan and India to share information on Chinese ship locations.
