One of the basic problems facing military commanders at all levels is deciding how to allocate available forces to accomplish desired objectives. A guiding concept in this sort of decision-making is economy of force, one of the fundamental and enduring principles of war. As defined in the 1954 edition of U.S. Army Field Manual FM 100-5, Field Service Regulations, Operations (which Trevor Dupuy believed contained the best listing of the principles):
Economy of Force
Minimum essential means must be employed at points other than that of decision. To devote means to unnecessary secondary efforts or to employ excessive means on required secondary efforts is to violate the principle of both mass and the objective. Limited attacks, the defensive, deception, or even retrograde action are used in noncritical areas to achieve mass in the critical area.
How do leaders determine the appropriate means for accomplishing a particular mission? The risk of failing to assign too few forces to a critical task is self-evident, but is it possible to allocate too many? Determining the appropriate means in battle has historically involved subjective calculations by commanders and their staff advisors of the relative combat power of friendly and enemy forces. Most often, it entails a rudimentary numerical comparison of numbers of troops and weapons and estimates of the influence of environmental and operational factors. An exemplar of this is the so-called “3-1 rule,” which holds that an attacking force must achieve a three to one superiority in order to defeat a defending force.
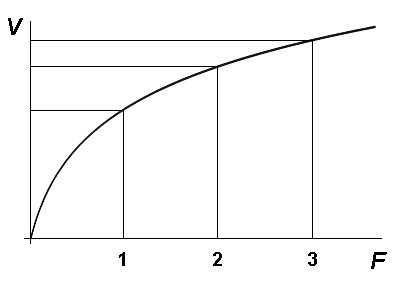
Through detailed analysis of combat data from World War II and the 1967 and 1973 Arab-Israeli wars, Dupuy determined that combat appears subject to a law of diminishing returns and that it is indeed possible to over-allocate forces to a mission.[1] By comparing the theoretical outcomes of combat engagements with the actual results, Dupuy discovered that a force with a combat power advantage greater than double that of its adversary seldom achieved proportionally better results than a 2-1 advantage. A combat power superiority of 3 or 4 to 1 rarely yielded additional benefit when measured in terms of casualty rates, ground gained or lost, and mission accomplishment.
Dupuy also found that attackers sometimes gained marginal benefits from combat power advantages greater than 2-1, though less proportionally and economically than the numbers of forces would suggest. Defenders, however, received no benefit at all from a combat power advantage beyond 2-1.
Two human factors contributed to this apparent force limitation, Dupuy believed, Clausewitzian friction and breakpoints. As described in a previous post, friction accumulates on the battlefield through the innumerable human interactions between soldiers, degrading combat performance. This phenomenon increases as the number of soldiers increases.
A breakpoint represents a change of combat posture by a unit on the battlefield, for example, from attack to defense, or from defense to withdrawal. A voluntary breakpoint occurs due to mission accomplishment or a commander’s order. An involuntary breakpoint happens when a unit spontaneously ceases an attack, withdraws without orders, or breaks and routs. Involuntary breakpoints occur for a variety of reasons (though contrary to popular wisdom, seldom due to casualties). Soldiers are not automatons and will rarely fight to the death.
As Dupuy summarized,
It is obvious that the law of diminishing returns applies to combat. The old military adage that the greater the superiority the better, is not necessarily true. In the interests of economy of force, it appears to be unnecessary, and not really cost-effective, to build up a combat power superiority greater than two-to-one. (Note that this is not the same as a numerical superiority of two-to-one.)[2] Of course, to take advantage of this phenomenon, it is essential that a commander be satisfied that he has a reliable basis for calculating relative combat power. This requires an ability to understand and use “combat multipliers” with greater precision than permitted by U.S. Army doctrine today.[3] [Emphasis added.]
NOTES
[1] This section is drawn from Trevor N. Dupuy, Understanding War: History and Theory of Combat (New York: Paragon House, 1987), Chapter 11.
[2] This relates to Dupuy’s foundational conception of combat power, which is clearly defined and explained in Understanding War, Chapter 8.
[3] Dupuy, Understanding War, p. 139.
